Orbital Implants and Ocular Prostheses
April 20, 2014An oculoplastic surgeon performing an Enucleation of the eye procedure.
Removal of the eye by enucleation or evisceration can relieve pain and minimize further risk to life and well-being of an individual with the above noted conditions. In addition, procedures to remove the eye should address the resultant appearance of the orbit. Orbital implants and ocular prostheses are used by the surgeon to restore a more natural appearance.
An orbital implant is placed after removal of the eye to restore volume to the eye socket and enhance movement or motility of an ocular prosthesis and eyelids. The eyeball is a slightly elongated sphere with a diameter of approximately 24 millimetres. To avoid a sunken appearance to the eye socket, an implant approximating this volume can be placed into the space of the removed eye, secured, and covered with Tenon's capsule and conjunctiva (the mucous membrane covering the natural sclera). Implants can be made of many materials with the most common being plastic,hydroxylapatite, metal alloy or glass.
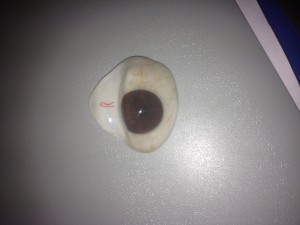
Later, once the conjunctiva have healed and post-operative swelling has subsided, an ocular prosthesis can be placed to provide the appearance of a natural eye. The prosthesis is fabricated by an ocularist. Its form is that of a cupped disc so that it can fit comfortably in the pocket behind the eyelids overlying the conjunctiva that covers the orbital implant. The external portion of the ocular prosthesis is painted and finished to mimic a natural eye color, shape and luster. It can be removed and cleaned periodically by the individual or a care giver.
The two part system of orbital implant and ocular
prosthesis provides a stable, and well tolerated aesthetic restoration of the
eye socket. Although vision is not restored by removal of the eye with
placement of an orbital implant and ocular prosthesis, a natural appearance can
result. The implant can be moved by intact extraocular muscles that will track
or move simultaneously with the other eye. The visible ocular prosthesis can
couple with the orbital implant and thus move simultaneously with the other
eye. The eyelids can move and blink over the prosthesis as well.
Posted by Kuldeep Raizada. Posted In : Ophthalmology







 Kuldeep Raizada completed his basic optometry education at Gandhi Eye Hospital, Aligarh, and has his training at L V Prasad Eye Institute, Hyderabad. where he was also Founder and Head of the Department of Ocular Prosthesis services till 2009. He completed a second fellowship, in Anaplastolgy, at MD Anderson Cancer Centre, Houston. He has also been trained by the top most ocularist and anaplastologist in United States of America.
His clinical interests include ocular and facial prosthesis, particularly in pediatric patients. His research interests lie in newer advancement in development of new types of prosthesis, newer solution for ptosis corrective glasses.
Kuldeep Raizada, is Founder & Director of the International Prosthetic Eye Center since 2010, where he is practicing since 2010.
Kuldeep Raizada has been recognized by the American Society of Ocularist, USA and American Anaplastology Association,USA and by several other professional organizations, for his excellence in research and clinical practice.
Kuldeep Raizada, have completed all requirements by American Society of Ocularist, which is hard work of 14000 working hours as well extensive study for prosthetics, Hence awarded the Diplomate Ocularist from American Society of Ocularist, USA, 2012, Chicago, USA, which is the First ever received all over Asia Pacific & throughout Middle East so ever.
At present he is reviewer of several journals like Contact Lens & Anterior Eye, International Journal of Anaplastology, Oculoplasty & Reconstructive Surgery (OPRS) and Many others. He has published and presented world widely
Kuldeep Raizada completed his basic optometry education at Gandhi Eye Hospital, Aligarh, and has his training at L V Prasad Eye Institute, Hyderabad. where he was also Founder and Head of the Department of Ocular Prosthesis services till 2009. He completed a second fellowship, in Anaplastolgy, at MD Anderson Cancer Centre, Houston. He has also been trained by the top most ocularist and anaplastologist in United States of America.
His clinical interests include ocular and facial prosthesis, particularly in pediatric patients. His research interests lie in newer advancement in development of new types of prosthesis, newer solution for ptosis corrective glasses.
Kuldeep Raizada, is Founder & Director of the International Prosthetic Eye Center since 2010, where he is practicing since 2010.
Kuldeep Raizada has been recognized by the American Society of Ocularist, USA and American Anaplastology Association,USA and by several other professional organizations, for his excellence in research and clinical practice.
Kuldeep Raizada, have completed all requirements by American Society of Ocularist, which is hard work of 14000 working hours as well extensive study for prosthetics, Hence awarded the Diplomate Ocularist from American Society of Ocularist, USA, 2012, Chicago, USA, which is the First ever received all over Asia Pacific & throughout Middle East so ever.
At present he is reviewer of several journals like Contact Lens & Anterior Eye, International Journal of Anaplastology, Oculoplasty & Reconstructive Surgery (OPRS) and Many others. He has published and presented world widely
